
SCIENCE COOKIES
Science articles with chocolate chips
How do we know the age of the celestial bodies?
Published: 12/4/2021
Author: Andrea Garma
Importance of knowing the age of things
Humans, throughout their short individual journey - period of time existing in the universe - and relatively longer if one considers a collective period since the existence of the race itself, have had an avid fascination with the past and finding out the why of things. Although, this could apply for areas of study such as history, or paleontology, knowing the age of things allows us to obtain new pieces of a puzzle about the history and origin of the universe as we know it, therefore, also the way it works. However, to achieve that we need benchmarks and indicators that allow us to obtain that important knowledge. Some of them could be characteristics such as radiation, color, among others.
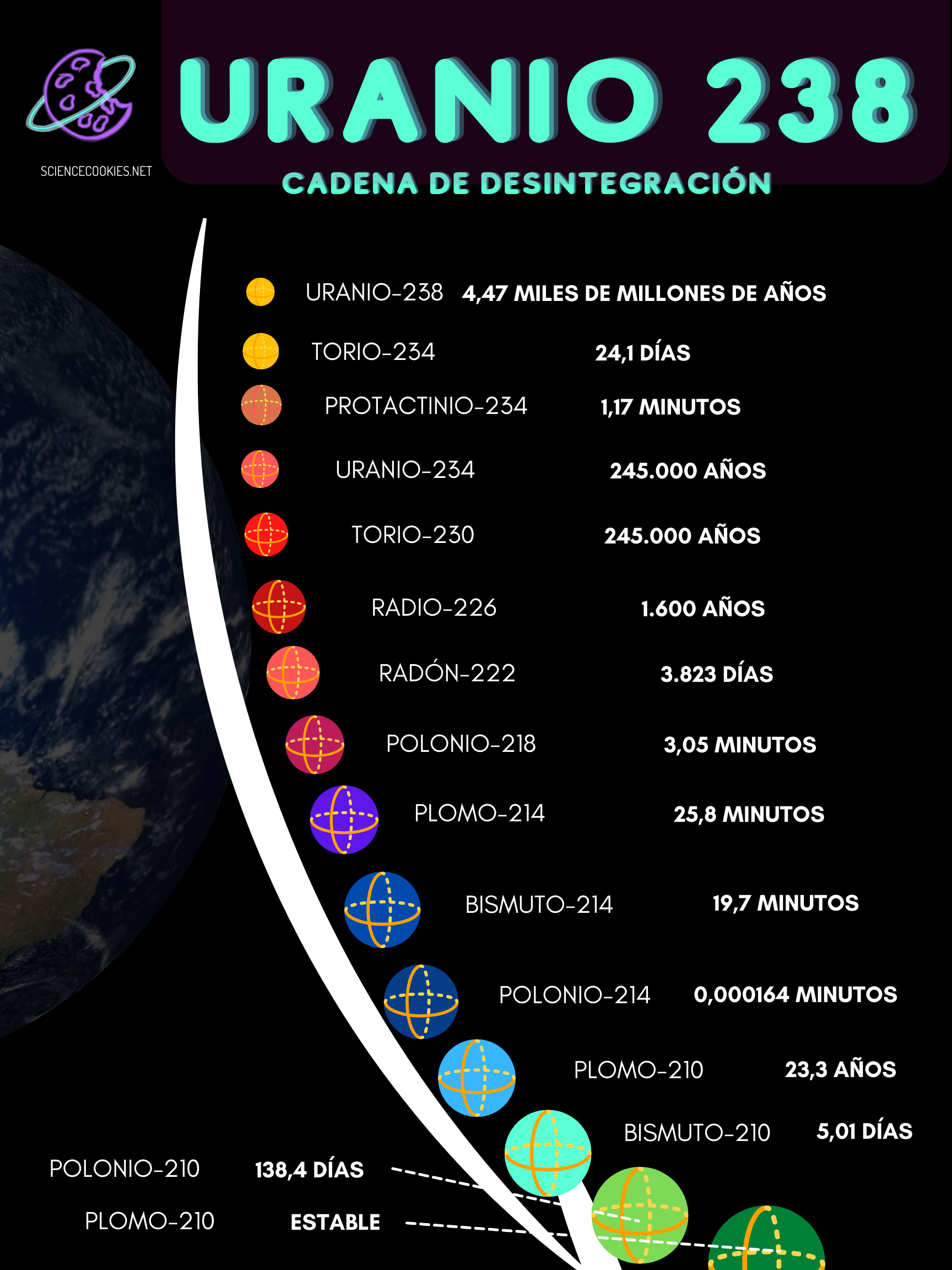
Age of a planet: Earth.
Determining the age of a planet can be considered a somewhat complicated task, in the first instance because in some cases, planets can renew or change their outer layers, as in the case of the earth. The earth has volcanoes that expel magma every certain time, which becomes a new rocky cover in it. The movement of the tectonic plates generates new mountains and, in the case of the oceanic floor, it is often renewed as the continents pass over it. Nonetheless, it is possible to know the age of planet Earth thanks to the ingenious uranium-lead dating method and zirconia. This wonderful mineral is extremely useful as it contains zirconium and small traces of uranium. The uranium atoms are similar enough to sometimes replace the place of the zirconium atoms in the crystal structure. However, uranium atoms are unstable and end up decaying into lead atoms. Knowing that lead could not have got there on its own, we can conclude that the more lead you find in a zirconia crystal, the older it will be. One of the oldest "pieces" we know of on earth is one of zirconia. Due to the conjectures made from the analysis of uranium-lead, it is possible to conclude that this planet is at least 4.4 billion years old. Similar tests with elements such as radiation can be applied to determine the age of other planets.
Age of a star
As for the age of a star, other methods are used to determine it. Recently a study presented at a meeting of the Astronomical Society of the USA in Seattle, exposed a new method of calculating the age by means of the speed of rotation. Specifically, it is used for smaller "cold" stars or the size of the sun. The most common in our galaxy. The method starts from the premise of how fast its movement is when the stars are young, but, like a spinning top, it slows down over time. The experiments were carried out thanks to the images provided by the Kepler space telescope.
On ages and the Universe
Although, now we know how the ages of certain astronomical objects can be measured, then ... How is it possible to measure the age of the Universe? The answer lies in the expansion of the Universe. Approximately 100 years ago it was believed that the universe had no beginning or end, therefore, knowing its age was a matter that no one asked, well, that most did not. It was Lemaître who formulated ideas about how wrong it was to think that the universe was eternal, and presented them to Einstein in 1927, but he commented that his physics, unlike how incredible his mathematics was, was abominable. However, Lemaître's ideas were confirmed thanks to the American Edwin Hubble , who realized that the Universe was expanding through the discovery of galaxies outside the Milky Way.
He managed to realize another indicator; galaxies moved faster the farther they were seen. However, the accounts that Hubble carried out led him to an incorrect age of 2,000 million years, at that time it was taken into account that the Universe was expanding and that process became increasingly slow. Before reaching the corrected age of the Universe, it is necessary to talk about supernovae, stars that are described as atomic bombs because they emit intense light, so intense that it allows us to see - for a short period of time - the deepest part of the Universe. Years later, a group of scientists, who were studying supernovae, came to the conclusion in 2011 that the expansion process of the universe was accelerating, and that in reality, the Universe was much older than previously believed, they even won the Nobel Prize. The age obtained after performing the calculations again was a little less than 14,000 million years.
References
https://scenio.es/como-saber-la-edad-de-un-planeta
https://www.bbc.com/mundo/noticias/2015/01/150106_ciencia_estrellas_velocidad_de_rotacion_hr
Soren Meibom, et al., “A Spin-Down Clock for Cool Stars from Observations of a 2.5-Billion-Year-Old Cluster,” Nature 517, 589–591 (29 January 2015); doi:10.1038/nature14118





